Previous Topic: Simple transaction with ganache using Golang
In the Previous topic, we learned how to do transaction with ganache using Golang. Now, we will learn what is smart contract and how to write smart contract and how to deploy it and how to call the contract using remix.
To learn what is smart contract, we already write a blog about that. Please feel free to take a look. Ethereum Smart contract.
For beginners, use the Remix IDE for learning smart contract and understand how it works. Then we will use Truffle framework.
REMIX: Remix IDE Link
Remix will provide a default workspace for developing smart contract. Now you can able to create a new file and start writing contracts, compile it with solidity compiler and deploy that contract and test the contracts.
Simple Smart Contract:
First create new file called store.sol and start writing a simple contract.
Contract Functionality:
- Store a record using SetRecord method.
- View the latest record. [record variable is public which helps us to view the latest record]
// SPDX-License-Identifier: GPL-3.0
pragma solidity ^0.8.10;
contract store{
string public record;
function SetRecord(string memory _record) public{
record = _record;
}
}Compile the smart contract using the solidity compiler.If the compilation successful, deploy the contract. Here in remix, we have multiple set of environments listed we can use those to deploy and call the contract. But the blockchain data is not stored once you refresh it. To know more about these environments remix env docs.
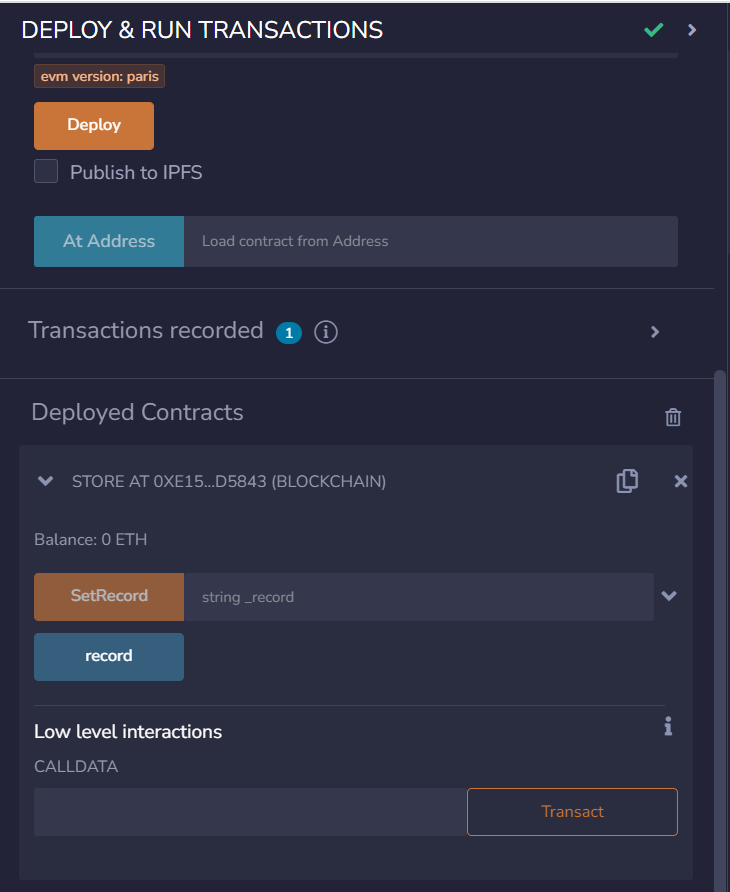
Now we are going to connect our local ganache network with the remix. First click the Custom - External Http Provider and provide the RPC server http://127.0.0.1:7545.
After the connection with our local ganache deploy the contract. Now check whether the contract deployed on the ganache.
Contract Address: 0xe1540EAa5cFE12210A217152885bE30D269d5843








Comments
Post a Comment